
According to USGS, a relatively weak earthquake struck central Arkansas at 3:51 am. The magnitude 2.0 event struck from a depth of 5.7 km north of Little Rock near the town of Guy, Arkansas. There were no reports of damage or injuries. USGS says there was no other seismic activity within 25 miles of today’s earthquake over the last 3 weeks.
According to USGS, earthquakes with a magnitude of 2.0 or less are rarely felt or heard by people, but once they exceed 2.0 , more and more people can feel them. While damage is possible with magnitude 3.0 events or greater, significant damage and casualties usually don’t occur until the magnitude of a seismic event rises to a 5.5 or greater rated event.
The area is involved in the fracking industry and it is not known whether today’s earthquake is related to that. Fracking, also known as hydraulic fracturing, is done in Arkansas, primarily in the Fayetteville Shale formation. This process is used to extract natural gas from the shale and accounts for a significant portion of the state’s gas production. While fracking offers economic benefits, it also raises environmental concerns, including water usage and potential for earthquakes.
Fracking-generating earthquakes have been a concern in places like Oklahoma and could also become problematic for other areas involved in the energy industry. Beginning in 2009, Oklahoma experienced a surge in seismicity according to USGS. “This surge was so large that its rate of magnitude 3 and larger earthquakes exceeded California’s from 2014 through 2017,” writes USGS in a report analyzing the increase in seismicity here. “While these earthquakes have been induced by oil and gas related process, few of these earthquakes were induced by fracking. The largest earthquake known to be induced by hydraulic fracturing in Oklahoma was a M3.6 earthquakes in 2019. The largest known fracking induced earthquake in the United States was a M4.0 earthquake that occurred in Texas in 2018. The majority of earthquakes in Oklahoma are caused by the industrial practice known as “wastewater disposal”. Wastewater disposal is a separate process in which fluid waste from oil and gas production is injected deep underground far below ground water or drinking water aquifers. In Oklahoma over 90% of the wastewater that is injected is a byproduct of oil extraction process and not waste frack fluid.”
While Arkansas is home to some fracking activity, it is also near the New Madrid Seismic Zone or NMSZ for short.
December 16 marks the anniversary of first of three very significant earthquakes to strike this region during the winter of 1811-1812, a violent time in seismological history of the region that scientists say will be repeated again. While this latest earthquake was relatively inconsequential, authorities are concerned that people aren’t properly prepared for when a big earthquake will strike this region. The matter of a larger destructive earthquake in this area is more of a matter of “when” rather than “if.” These recent earthquakes have been in the heart of the NMSZ where a significant earthquake will likely happen again at some point in the future.
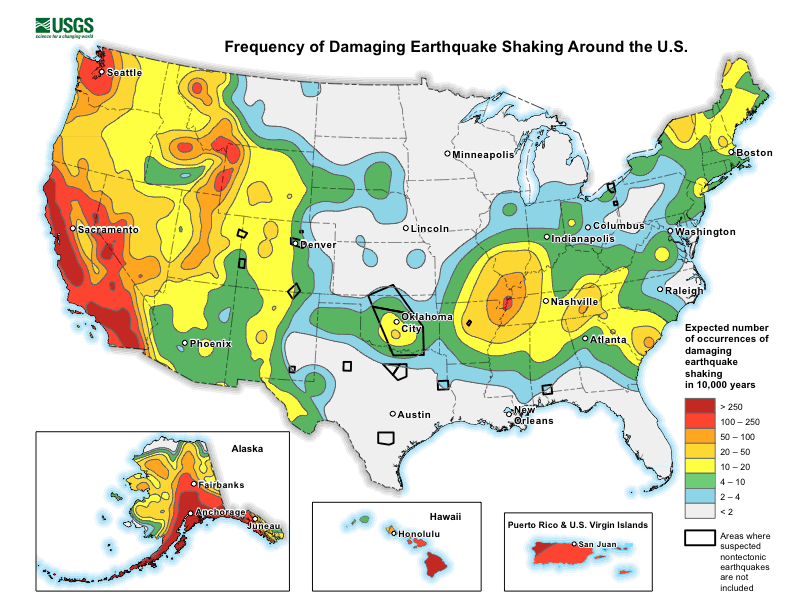
While the US West Coast is well known for its seismic faults and potent quakes, many aren’t aware that one of the largest quakes to strike the country actually occurred near the Mississippi River. On December 16, 1811, at roughly 2:15am, a powerful 8.1 quake rocked northeast Arkansas in what is now known as the New Madrid Seismic Zone. The earthquake was felt over much of the eastern United States, shaking people out of bed in places like New York City, Washington, DC, and Charleston, SC. The ground shook for an unbelievably long 1-3 minutes in areas hit hard by the quake, such as Nashville, TN and Louisville, KY. Ground movements were so violent near the epicenter that liquefaction of the ground was observed, with dirt and water thrown into the air by tens of feet. President James Madison and his wife Dolly felt the quake in the White House while church bells rang in Boston due to the shaking there.
But the quakes didn’t end there. From December 16, 1811 through to March of 1812, there were over 2,000 earthquakes reported in the central Midwest with 6,000-10,000 earthquakes located in the “Bootheel” of Missouri where the New Madid Seismic Zone is centered.
The second principal shock, a magnitude 7.8, occurred in Missouri weeks later on January 23, 1812, and the third, a 8.8, struck on February 7, 1812, along the Reelfoot fault in Missouri and Tennessee.
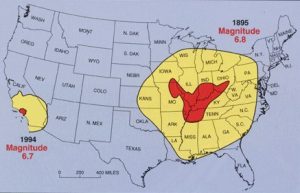
The second principal shock, a magnitude 7.8, occurred in Missouri weeks later on January 23, 1812, and the third, a 8.8, struck on February 7, 1812, along the Reelfoot fault in Missouri and Tennessee.
The main earthquakes and the intense aftershocks created significant damage and some loss of life, although lack of scientific tools and news gathering of that era weren’t able to capture the full magnitude of what had actually happened. Beyond shaking, the quakes also were responsible for triggering unusual natural phenomena in the area: earthquake lights, seismically heated water, and earthquake smog.
Residents in the Mississippi Valley reported they saw lights flashing from the ground. Scientists believe this phenomena was “seismoluminescence”; this light is generated when quartz crystals in the ground are squeezed. The “earthquake lights” were triggered during the primary quakes and strong aftershocks.
Water thrown up into the air from the ground, or the nearby Mississippi River, was also unusually warm. Scientists speculate that intense shaking and the resulting friction led to the water to heat, similar to the way a microwave oven stimulates molecules to shake and generate heat. Other scientists believe as the quartz crystals were squeezed, the light they emit also helped warm the water.
During the strong quakes, the skies turned so dark that residents claimed lit lamps didn’t help illuminate the area; they also said the air smelled bad and was hard to breathe. Scientists speculate this “earthquake smog” was caused by dust particles rising up from the surface, combining with the eruption of warm water molecules into the cold winter air. The result was a steamy, dusty cloud that cloaked the areas dealing with the quake.
The February earthquake was so intense that boaters on the Mississippi River reported that the flow of the water there reversed for several hours.
The area remains seismically active and scientists believe another strong quake will impact the region again at some point in the future. Unfortunately, the science isn’t mature enough to tell whether that threat will arrive next week or in 50 years. Either way, with the population of New Madrid Seismic Zone huge compared to the sparsely populated area of the early 1800s, and tens of millions more living in an area that would experience significant ground shaking, there could be a very significant loss of life and property when another major quake strikes here again in the future.