Due to an increase in earthquake activity in Hawaii, USGS announced early today that they will be increasing their public reports on Kilauea Volcano from weekly to daily until an eruption occurs …or until seismic activity relaxes. While seismic activity has increased, Kilauea volcano is not erupting at this moment.
“Continued summit inflation and an uptick in earthquake activity over the past week suggests an increasing amount of magma is being stored beneath the summit area. Given activity over the past week, HVO will switch from weekly updates to daily updates starting Wednesday December 18,” USGS Volcanoes said in a statement.
HVO is short for Hawaiian Volcano Observatory which is part of USGS that monitors and studies volcanoes and earthquakes in Hawaii and American Samoa. According to HVO, their mission is to assess hazards, issue warnings, advance scientific understanding, reduce the impacts of volcanic eruptions, and communicate results to the public, emergency managers, and the scientific community.

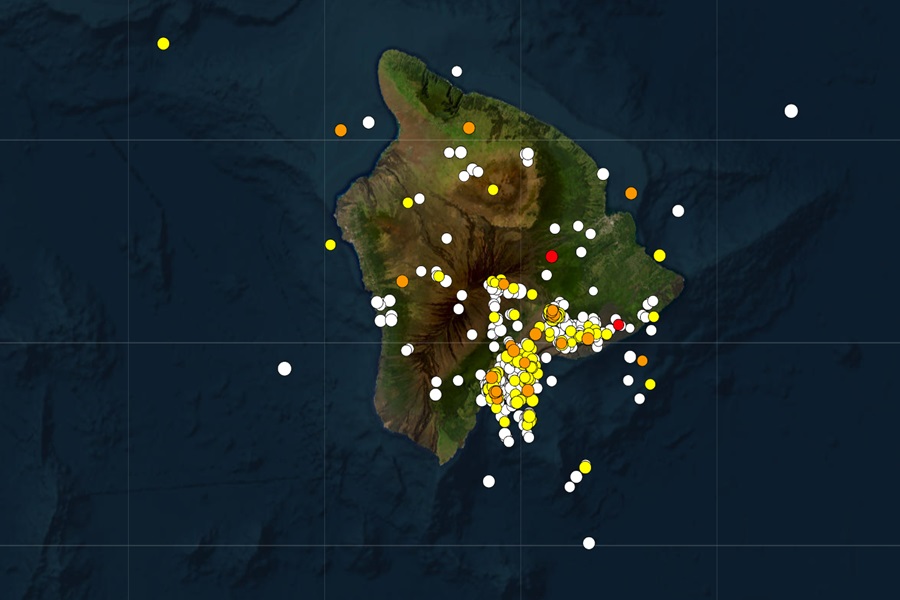
According to USGS, there have been 720 earthquakes around Hawaii over the last 30 days, with all but two happening on the Big Island or nearby adjacent waters. In the last 7 days, there have been 159 measured earthquakes on/around the Big Island; in the last 24 hours, there were 25 earthquakes. The largest earthquake of the bunch was a magnitude 4.0 event which struck near the town of Volcano, Hawaii on the morning of November 30.
Earthquake activity at Kilauea’s summit region was low in the first half of the last week, HVO said in today’s update. “Between the early morning of Saturday December 14 and December 17, there were several modest upticks in seismic activity underneath the volcano’s summit, lasting from an hour to a few hours, often accompanied by minor inflation as recorded at the tiltmeter at Uēkahuna, northwest of Kaluapele, the summit caldera, and tiltmeter at Sand Hill, southwest of Kaluapele.”
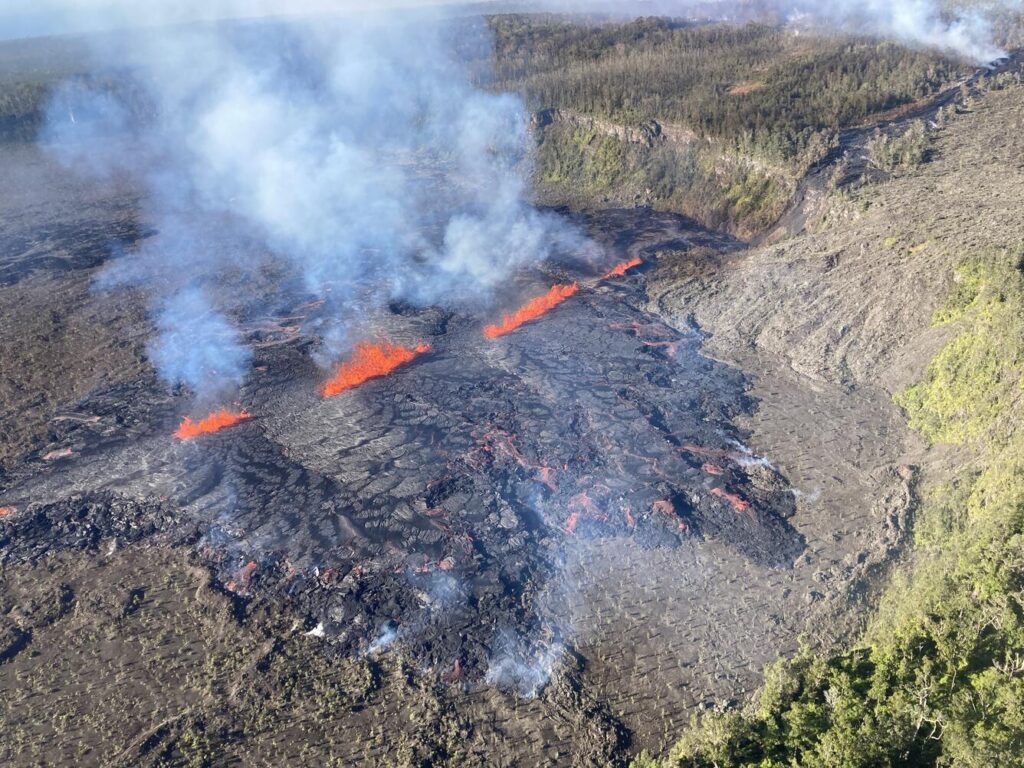

Since the September eruption in the East Rift Zone (EFZ), there have been sustained rates of inflation at the summit. The most recent measurement of the sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rate from the summit was approximately 70 tonnes per day on October 17, a value representative of noneruptive conditions at Kilauea. The volcano briefly erupted in and near the Napau Crater from September 15-20, covering more than 880,000 square meters or 217 acres of lava.
Since that most recent eruption, unrest has continued at low levels at the summit and on the ERZ of Kilauea. Rates of seismicity and ground deformation have greatly decreased since the eruption, but geophysical data show that magma is continuing to move at a low rate into the volcano.
“Future intrusions and eruptions could occur with continued magma supply,” cautions HVO, but they are clear to stress the volcano isn’t erupting now or are their signals that an eruption is imminent.

In the U.S., the USGS and volcano observatory units are responsible for issuing Aviation Codes and Volcanic Activity Alert Levels. Aviation Codes are green, yellow, orange, or red. When ground-based instrumentation is insufficient to establish that a volcano is at a typical background level of activity, it is simply “unassigned.” While green means typical activity associated with a non-eruptive state, yellow means a volcano is exhibiting signs of elevated unrest above known background levels. When a volcano exhibits heightened or escalating unrest with the increased potential of eruption, it jumps to orange. Finally, when an eruption is imminent with significant emission of volcanic ash expected in the atmosphere or an eruption is underway with significant emission of volcanic ash into the atmosphere, the code becomes red. Volcanic Activity Alert levels are normal, advisory, watch, or warning. As with aviation codes, if data is insufficient, it is simply labeled as “unassigned.” When the volcano is at typical background activity in a non-eruptive state, it is considered normal. If the volcano exhibits signs of elevated unrest above background level, an advisory is issued. If a volcano exhibits heightened or escalating unrest, a watch is issued while a warning is issued when a hazardous eruption is imminent.
For now, scientists are putting the Kilauea volcano at an “ADVISORY” alert level while the current aviation color code is “YELLOW.”