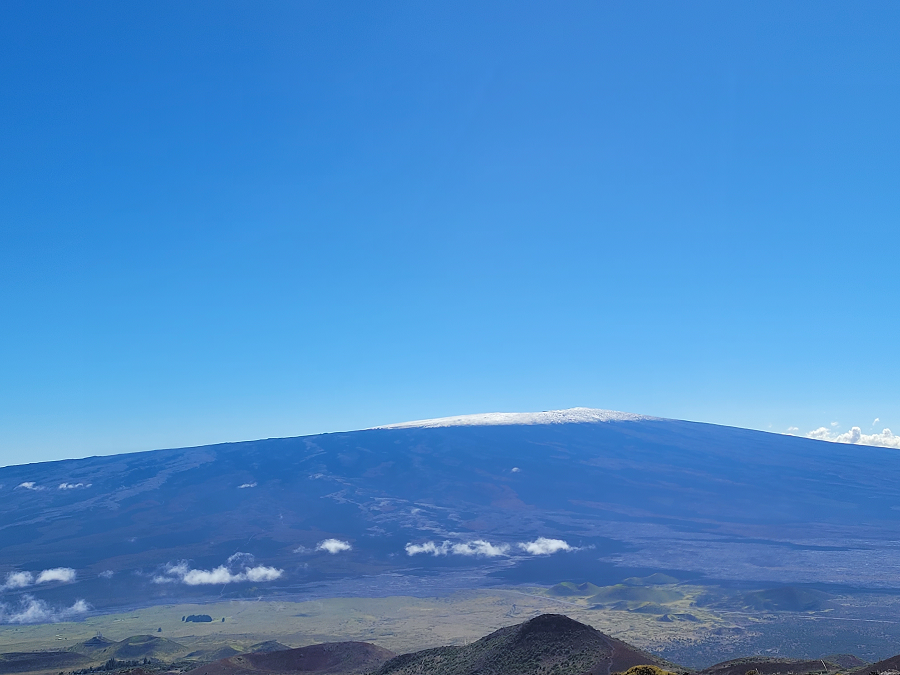

While it isn’t erupting right now, ongoing unrest at the world’s largest volcano has prompted local authorities to remind residents and visitors to prepare for the eventual eruption. In an April 27 posting made by the Civil Defense Agency for Hawaii County, also known as “The Big Island”, authorities are suggesting now is a good time for those in the hazard zones that surround Mauna Loa volcano to prepare for the inevitable. According to Hawaii County Civil Defense, Mauna Loa has seen an uptick in activity, including 175 small-magnitude earthquakes below Mauna Loa in the last week alone.
The comments from Civil Defense come just weeks after scientists with the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) at USGS cautioned, “While an eruption of Mauna Loa is not imminent, now is the time to revisit personal eruption plans. Similar to preparing for hurricane season, having an eruption plan in advance helps during an emergency.”
The role of the Civil Defense Agency is to direct and coordinate the development and administration of the County’s total emergency preparedness and response program to ensure prompt and effective action when natural or man-caused disaster threatens or occurs anywhere in the County of Hawaii.
Mauna Loa is considered the largest active volcano on Earth, rising to 13,681 feet above sea level. Mauna Loa rises up from the ocean floor of the Central Pacific at a depth of about 3 miles. Because of the volcano’s significant mass, the ocean floor directly beneath Mauna Loa is depressed by another 5 miles. According to USGS, this places Mauna Loa’s summit about 56,000 feet above its base; the enormous volcano covers half of the island of Hawaii, also known simply as the “Big Island of Hawaii.”
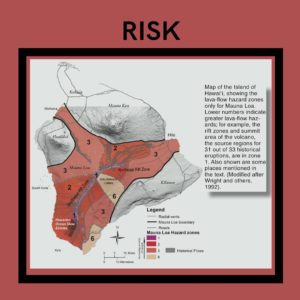
Mauna Loa eruptions tend to produce voluminous, fast-moving lava flows that can impact communities on the east and west sides of the Big Island from Kona to Hilo. Since the 1850s, Hilo in eastern Hawaii has been threatened by 7 Mauna Loa lava flows. On the south and west sides of the island, Mauna Loa lava flows have reached the coast there 8 times: in 1859, 1868, 1887, 1926, 1919, and three times in 1950.
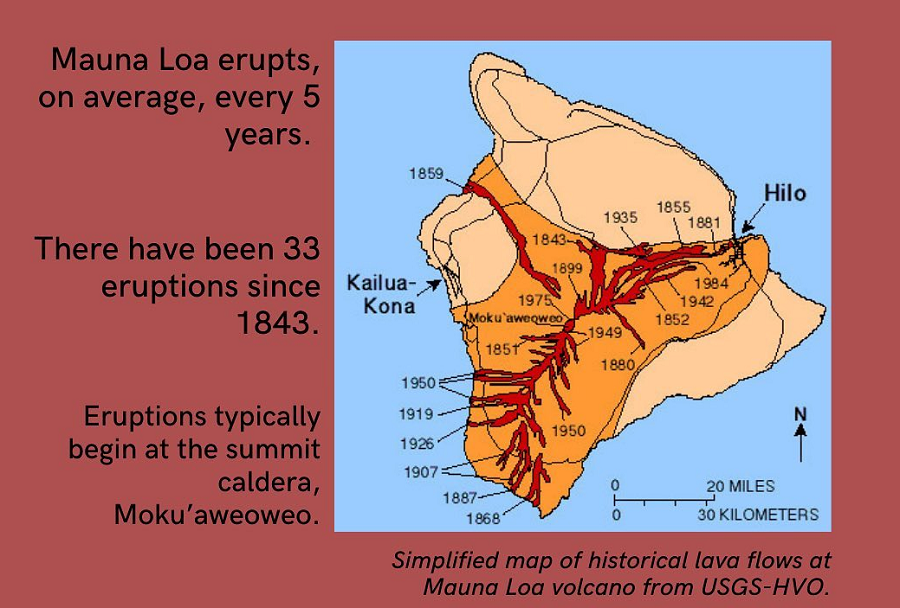
According to USGS, while Mauna Loa is not erupting right now , rates of deformation and seismicity remain elevated above long-term background levels. GPS measurements continue to show slow, long-term summit inflation consistent with magma supply to the volcano’s shallow storage system. A slight increase in the rate of inflation that began in January continues.
With another eruption on Mauna Loa inevitable, although the timing is not yet defined, the USGS is urging people on Hawaii to have a personal response plan, prepare a “go bag”, and determine what one would do in the event of an eruption at different times of the day or week.
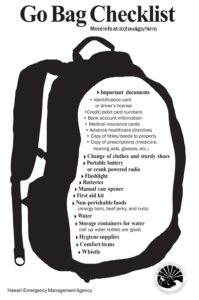
“The most important thing you can do is to have a personal response plan,” says the USGS. Document what you’d do when a volcano erupts and make sure your family and friends are aware of what that plan is.
USGS suggests getting a “go bag” in order. “Nowadays, people pack “go” bags containing essential items in case you have to leave your house under an evacuation order. You may want to include important documents, like your birth certificate, deeds, legal papers, and medications.”
USGS says people in Hawaii should develop plans that factor in different types of days and time of day: if family members are at work or school at specific times, the plan should address what people should do and how they should communicate if an eruption occurs when people aren’t home. USGS says, “It is useful to also have a communication plan, so you can be in touch with those you care about.”
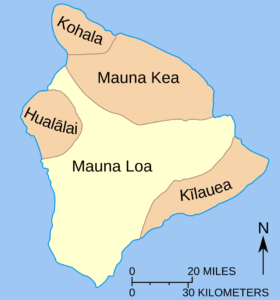
Mauna Loa is one of 5 volcanoes that make up Hawaii’s Big Island. The oldest volcano on Hawaii Island is Kohala, which is more than one million years old. Kilauea is the youngest, at an estimated 300,000-600,000 years old. Mauna Loa is the second youngest volcano on the island, estimated to be about 700,000 years old.