A magnitude 2.8 earthquake struck outside of Elgin, South Carolina this morning in an area that saw a mysterious swarm of earthquakes at the end of 2021 and in much of 2022 and 2023. According to USGS, the earthquake struck just outside of Elgin, South Carolina at 9:27 am this morning. More than 950 people reported to USGS they felt this earthquake using the USGS “Did you feel it?” website reporting tool. However, the quake was much too weak to create any damage or injuries. Today’s earthquake was the third to strike this area this year.
Several dozen earthquakes have struck seismically active South Carolina since December of 2021. The mysterious swarm began on Monday, December 27, at 2:18 pm in the afternoon. That first 3.3 magnitude earthquake hit 30 miles north of Columbia, South Carolina at a depth of only 3.1 km. More than 3,100 residents reported to USGS they felt it at the time, with one report of shaking coming from as far away as Rock Hill, which is at the North/South Carolina state border. While many felt the earthquake, there was no reported damage in the Palmetto State. That earthquake was followed by 10 more ranging in intensity between a magnitude 1.5 to a magnitude 2.6 event. The second earthquake struck three hours twenty minutes after the first one. The last earthquake in that series struck on the morning of January 5, bringing a temporary end to the earthquakes there. But the swarm returned many times throughout 2022, rattling locals and unnerving local officials that weren’t sure of their source or cause.
According to USGS, a swarm is a sequence of mostly small earthquakes with no identifiable mainshock. “Swarms are usually short-lived, but they can continue for days, weeks, or sometimes even months,” USGS adds. However, the Elgin-area South Carolina event doesn’t fit the typical definition of a swarm since the first event was substantially larger than the rest. This recent swarm doesn’t fit in a typical swarm pattern either.
According to the South Carolina Emergency Management Division (SCEMD), there are approximately 10-15 earthquakes every year in South Carolina, with most not felt by residents; on average, only 3-5 are felt each year. Most of South Carolina’s earthquakes are located in the Middleton Place-Summerville Seismic Zone. The two most significant historical earthquakes to occur in South Carolina were the 1886 Charleston-Summerville quake and the 1913 Union County quake. The 1886 earthquake in Charleston was the most damaging earthquake to ever occur in the eastern United States; it was also the most destructive earthquake in the U.S. during the 19th century.
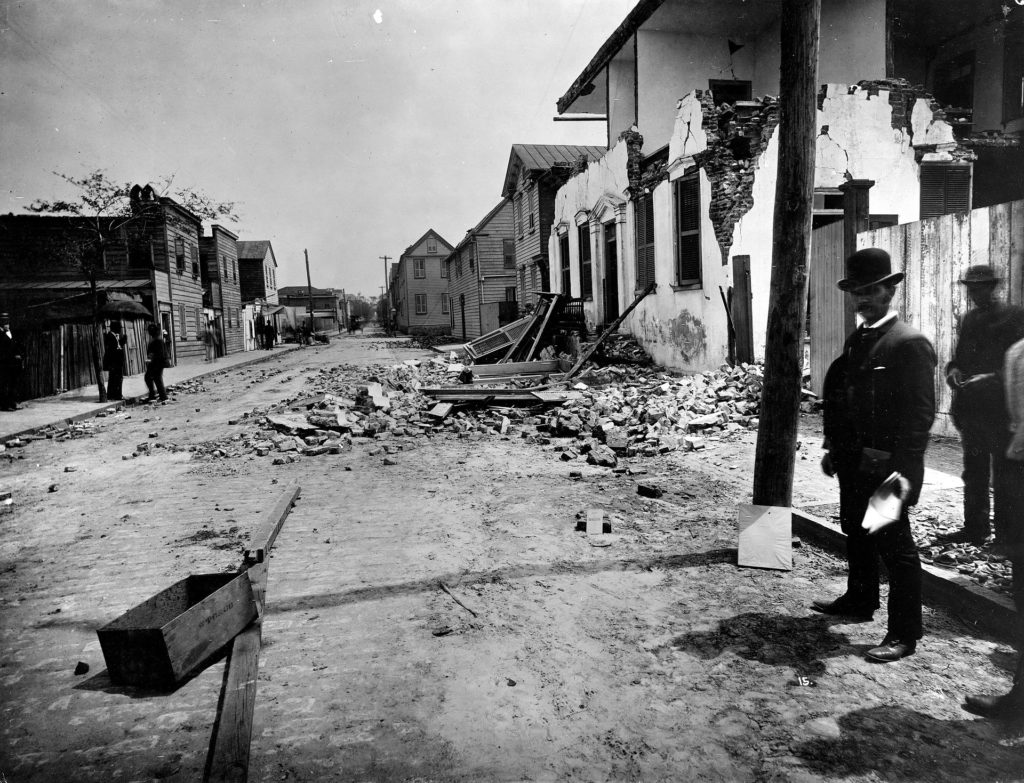

The 1886 earthquake struck at about 9:50 pm on August 31; it was estimated to have been rated a magnitude 6.9 – 7.3 seismic event. The earthquake was felt as far away as Boston, Massachusetts to the north, Chicago, Illinois and Milwaukee, Wisconsin, to the northwest, and New Orleans, Louisiana to the south. The earthquake energy even traveled as far away as Cuba and Bermuda, where some shaking was felt too. The initial earthquake lasted about 45 seconds.
The 1886 Charleston earthquake was responsible for 60 deaths and over $190 million (in 2023 dollars) in damage. The area of major damage extended out 60-100 miles from the epicenter, with some structural damage even reported in central Alabama, Ohio, eastern Kentucky, southern Virginia, and western West Virginia from the initial quake.
A study published in 2008 in the Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering hypothesized that if such an earthquake were to strike the region today, it would lead to approximately 900 deaths, 44,000 injuries, and damages in excess of $20 billion in South Carolina alone.
The initial earthquake was followed by an aftershock 10 minutes later; over the first 24 hours, seven additional strong aftershocks hit. Over the following 30 years, a total of 435 aftershocks were measured.
According to USGS, since at least 1776, people living inland in North and South Carolina, and in adjacent parts of Georgia and Tennessee, have felt small earthquakes and suffered damage from infrequent larger ones. The largest earthquake in this inland area was a magnitude 5.1 event which occurred in 1916. Moderately damaging earthquakes strike the inland Carolinas every few decades, and smaller earthquakes are felt about once each year or two.
Earthquakes in the central and eastern U.S., although less frequent than in the western U.S., are typically felt over a much broader region. East of the Rockies, an earthquake can be felt over an area as much as ten times larger than a similar magnitude earthquake on the west coast. A magnitude 4.0 eastern U.S. earthquake typically can be felt at many places as far as 60 miles from where it occurred, and it infrequently causes damage near its source. A magnitude 5.5 eastern U.S. earthquake usually can be felt as far as 300 miles from where it occurred, and sometimes causes damage as far away as 25 miles away.