
The concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide, also known as “CO2”, surged to 421.21 parts per million (PPM) this week, breaking records for the greatest amount recorded since records began in the 1950s.
Located at the Mauna Loa Observatory (MLO) on the Big Island of Hawaii, the research facility run by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) collects daily CO2 measurements. The MLO is considered to be the gold standard for measuring CO2 in the Earth’s atmosphere around the globe.
The MLO is located on the north flank of Mauna Loa Volcano at an elevation of 11,135 feet above sea level. Mauna Loa is also considered the world’s largest active volcano. The observatory has been continuously monitoring and collecting data related to atmospheric change since the 1950’s. Because of the observatory’s location not far from the summit of the active volcano, instruments there usually protrude through the strong marine temperature inversion layer present in the region, which separates the more polluted lower portions of the atmosphere from the much cleaner free troposphere. According to NOAA, the undisturbed air, remote location, and minimal influences of vegetation and human activity at MLO are ideal for monitoring constituents in the atmosphere that could impact global climate.
Beyond CO2, the MLO facility also measures greenhouse gases, halocarbons, and other ozone depleting gases.
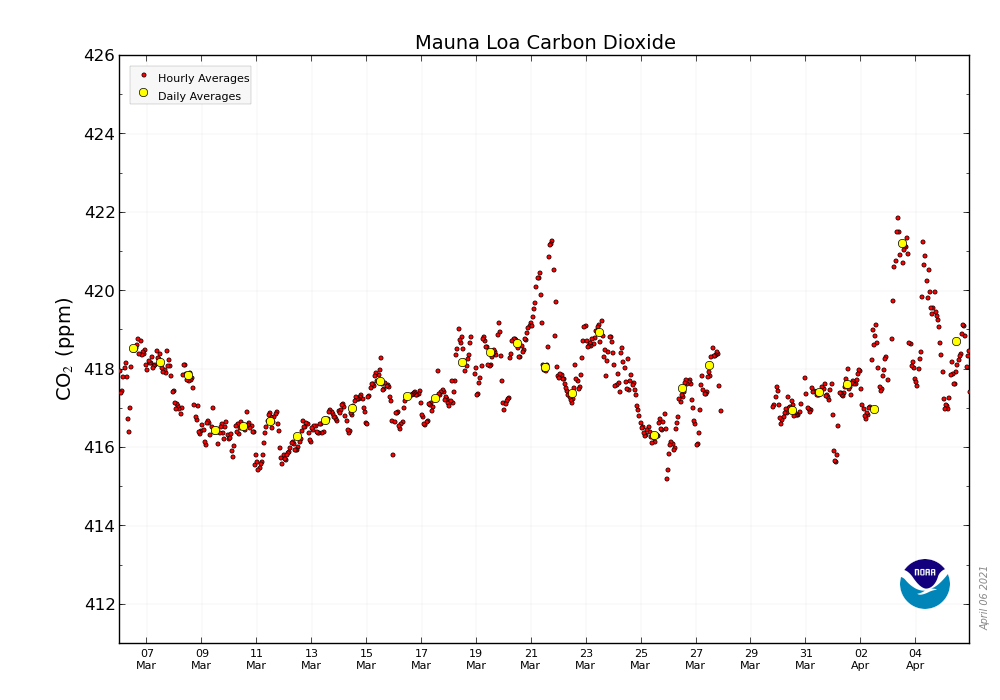
During the global pandemic in 2020, an abrupt reduction in carbon dioxide emissions occurred around the world, with a significant reduction in flying, driving, and industrial output. While the carbon emission declines were significant, up to 25% in some regions, there doesn’t appear to be any lingering impact to the growing CO2 measurements at the MLO.
Scientists continue to explore what, if any, impact an increase in CO2 has on weather and climate. While a link between CO2 and climate isn’t yet certain, the rise in CO2 being measured at MLO is.