
The National Weather Service’s Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC) has issued Geomagnetic Storm Watch for Earth for Saturday. While aurora and some electrical, navigation, and communication issues are possible, this new event should be much less severe than the storm which struck Earth in April, illuminating a large part of the United States with a stunning, colorful aurora show. G1 level storm conditions are expected this time around.
According to the SWPC’s latest Forecast Discussion, a faint full-halo shock was first clearly observed in coronagraph imagery yesterday. Analysis, however, concluded no visible correlative activity was observed on the Earth-facing disk. Additional
activity included a large, active filament that eventually erupted. Modeling of this event indicates a bulk of the material will pass south of Earth with the shock and possible northern flanking edge of the magnetic cloud arriving early on July 15.
For now, the Earth’s geomagnetic field is expected to be primarily quiet to unsettled, with active conditions likely tomorrow due to any coronal mass ejection shock-related effects. Active conditions remain likely on Friday while G1 level storm conditions are possible Friday night into Saturday.
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) are large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun’s corona. They can eject billions of tons of coronal material and carry an embedded magnetic field, frozen in flux, that is stronger than the background solar wind interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) strength. CMEs travel outward from the Sun at various speeds, with some reaching the Earth as quickly as 15-18 hours and others requiring days to arrive. According to the SWPC, CMEs expand in size as they propagate away from the Sun and larger ones can reach a size comprising nearly a quarter of the space between Earth and the Sun by the time it reaches our planet.
As the CME interacts with Earth and its magnetosphere, a variety of things could unfold based on the amount of energy hitting and the angle it impacts the Earth.
Geomagnetic storms are rated on a 1-5 scale by the SWPC, with 1 considered minor and 5 considered extreme. Geomagnetic storms can disrupt electronics and electrical systems, interfere with spacecraft and satellite communication, and also trigger brilliant displays of the aurora in the night sky.
In the case of the G1 class storm due to hit Earth this weekend, weak power grid fluctuations could occur, especially at northern latitudes. Minor impacts on satellite operations could also be possible. Aurora could also be visible more south than it usually is; in this case, it could extend as far south as northern Michigan and Maine. Should the geomagnetic storm become stronger, aurora could be brighter and could appear even more south.
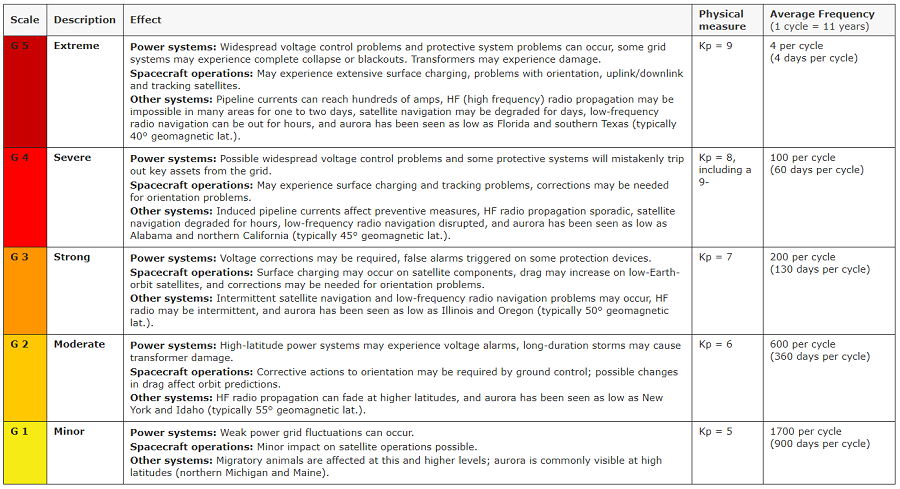

Image: NASA/Mary Pat Hrybyk-Keith

NOAA forecasters analyze a variety of solar data from spacecraft to determine what impacts a geomagnetic storm could produce. Analyzing data from the DSCOVER and ACE satellite is one way forecasters can tell when the enhanced solar wind from a coronal hole is about to arrive at Earth. A few things they look for in the data to determine when the enhanced solar wind is arriving at Earth:

• Solar wind speed increases
• Temperature increases
• Particle density decreases
• Interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) strength increases
While these solar events can help illuminate the sky with stunning aurora, they can also do considerable harm to electronics, electrical grids, and satellite and radio communications.
The 1859 incident, which occurred on September 1-2 in 1859, is also known as the “Carrington Event.” This event unfolded as powerful geomagnetic storm struck Earth during Solar Cycle 10. A CME hit the Earth and induced the largest geomagnetic storm on record. The storm was so intense it created extremely bright, vivid aurora throughout the planet: people in California thought the sun rose early, people in the northeastern U.S. could read a newspaper at night from the aurora’s bright light, and people as far south as Hawaii and south-central Mexico could see the aurora in the sky.
The event severely damaged the limited electrical and communication lines that existed at that time; telegraph systems around the world failed, with some telegraph operators reporting they received electric shocks.
A June 2013 study by Lloyd’s of London and Atmospheric and Environmental Research (AER) in the U.S. showed that if the Carrington event happened in modern times, damages in the U.S. could exceed $2.6 trillion, roughly 15% of the nation’s annual GDP.

While typically known for their weather forecasts, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and its National Weather Service (NWS) is also responsible for “space weather.” While there are private companies and other agencies that monitor and forecast space weather, the official source for alerts and warnings of the space environment is the Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC). The SWPC is located in Boulder, Colorado and is a service center of the NWS, which is part of NOAA. The Space Weather Prediction Center is also one of nine National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) as they monitor current space weather activity 24/7, 365 days a year.