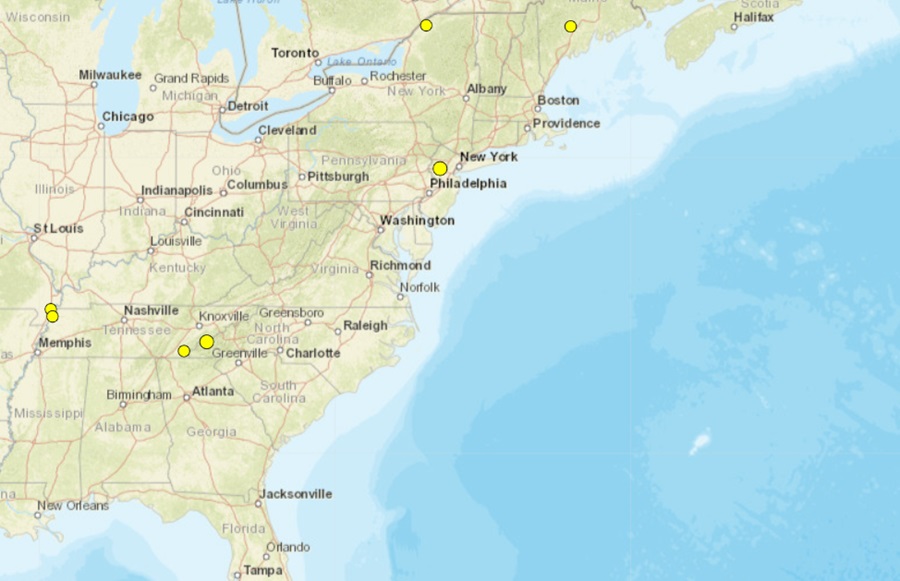
It’s been a seismically active last seven days across the eastern United States, with USGS reporting several earthquakes in states that include Tennessee, North Carolina, New Jersey, New York, and Maine. While Tennessee had the most earthquakes, New Jersey had the strongest. Fortunately all of the earthquakes have been relatively weak and caused no reported damage or injuries.
The New Jersey earthquake struck near Whitehouse Station in the northern part of the Garden State on Thursday. Striking at 3:00 pm from a depth of 5 km, USGS said dozens of people throughout northern New Jersey and eastern Pennsylvania felt it and reported so through the “Did you feel it?” reporting tool on their website. The earthquake was accompanied by a loud explosion-like noise; people reached out to police departments in Chester, Clinton, Lebanon, and Washington to see what had happened. This earthquake was centered along the Ramapo Fault line which separates the geological Highlands to the north from the Piedmont to the south, above the Coastal Plain.
The next strongest earthquake struck west-northwest of Bryson City in western North Carolina, not far from the Tennessee state line. The magnitude 2.0 event struck at 7:19 am on Friday in the heart of the Blue Ridge Mountains. This area has seen a few weak earthquakes in recent weeks.
According to the North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality, while North Carolina is no stranger to earthquakes, large, damaging earthquakes are rare. Large, damaging seismic events are rare and the few felt in North Carolina had epicenters outside of the state. Most quakes in North Carolina originate from the East Tennessee seismic zone to the west, the Charleston, South Carolina seismic zone to the south, or the Central Virginia seismic zone to the north. The most common and strongest earthquakes to strike the state have been in the western part along the Appalachian Mountains.
The North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) cautions that people in the state should be prepared for the possibility of larger quakes. “Although strong earthquakes here in North Carolina are infrequent, proper construction techniques need to be followed. An earthquake of magnitude 5 or greater could block major transportation routes in the mountains and cause structural damage elsewhere,” the DEQ writes. They add, “Many of the larger earthquakes in North Carolina occurred when the state was more rural. Recent development includes buildings and infrastructure such as road and power networks. Modern building codes take into account the possibility of an earthquake but many older buildings were not constructed to withstand violent shaking.”
Two earthquakes of equal magnitude struck northern New York and southern Maine. Both rated a magnitude 1.5 event, the Maine quake struck near Smithfield at 4:37 pm on Friday while the New York quake hit just north of Rensselaer Falls at 3:12 am on Saturday.
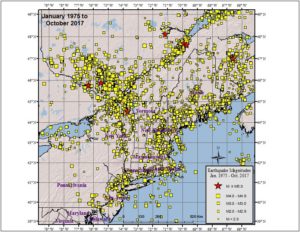
According to the Northeast States Emergency Consortium (NESEC), New York is a state with a very long history of earthquake activity that has touched all parts of the state. Since the first earthquake that was recorded in December 19, 1737, New York has had over 550 earthquakes centered within its state boundaries through 2016. It also has experienced strong ground shaking from earthquakes centered in nearby U.S. states and Canadian provinces. Most of the quakes in New York have taken place in the greater New York City area, in the Adirondack Mountains region, and in the western part of the state.
While many of the earthquakes to hit New York are weak like yesterday’s, some have been damaging. Of the 551 earthquakes recorded between 1737 and 2016, 5 were considered “damaging”: 1737, 1929, 1944, 1983, and 2002.
While not famous for their earthquakes, Maine does get them from time to time. On August 8, 2023, a stronger magnitude 2.5 earthquake struck not far from where today’s was. On September 16 in 2022, another magnitude 2.3 earthquake struck near today’s. On April 24, 2022, an earthquake of similar intensity also struck central Maine. Earlier that month, on April 2, a magnitude 2.0 earthquake struck about 7 miles southeast of Waterville, near the Winslow-China town line. On March 8, a magnitude 2.1 earthquake struck about 2 miles north of Tunk Lake in eastern Hancock County. On February 12, a magnitude 2.4 earthquake struck 12 miles west of Houlton; some locals reported feeling shaking then. On February 4, a magnitude 2.9 event was widely felt in the Bethel area of western Maine, 8 miles from the epicenter in Gorham, New Hampshire. People up to 25 miles away from the epicenter of that earthquake felt it in Maine. Two earthquakes of a 2.0 magnitude hit on January 17 ; one was 2 miles west of Springvale, the other was about 1/2 mile south of Springvale.
The strongest earthquake to strike Maine in the last 10 years was a magnitude 4.5 event on October 16, 2012 in East Waterboro, about 13 miles northwest of Saco.
According to the Maine Geological Survey with the Department of Conservation, seismic activity in Maine is typical of the Appalachian region of northeastern North America. “There is a low but steady rate of earthquake occurrence,” they report, adding that “The earthquakes are presumably caused by modern stress being released occasionally along zones of weakness in the earth’s crust, but a more specific cause for the earthquake activity is not known.”
The remaining two earthquakes over the last 7 day struck Tennessee, with one near the western state line and the other near the easter state line. The eastern quake struck at 2:22 am from a depth of 5.1 km near Benton on Tuesday; it was rated a magnitude 1.7 event.
The western quake wasn’t far from a historic, violent earthquake series. December 16 marks the anniversary of the first of three major quakes to strike the United States during the winter of 1811-1812, a violent time in seismological history of the region that scientists say will be repeated again.
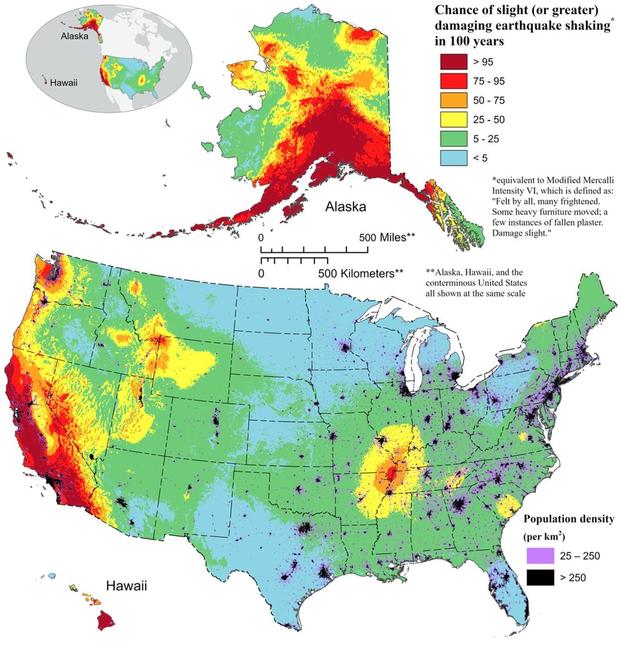
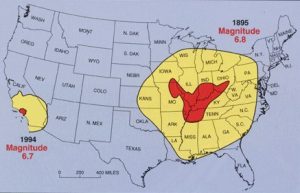
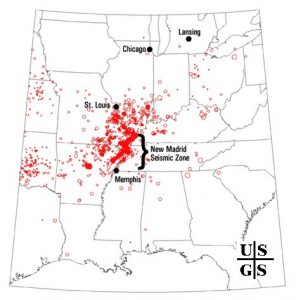
While the US West Coast is well known for its seismic faults and potent quakes, many aren’t aware that one of the largest quakes to strike the country actually occurred near the Mississippi River. On December 16, 1811, at roughly 2:15am, a powerful 8.1 quake rocked northeast Arkansas in what is now known as the New Madrid Seismic Zone (NMSZ). The earthquake was felt over much of the eastern United States, shaking people out of bed in places like New York City, Washington, DC, and Charleston, SC. The ground shook for an unbelievably long 1-3 minutes in areas hit hard by the quake, such as Nashville, TN and Louisville, KY. Ground movements were so violent near the epicenter that liquefaction of the ground was observed, with dirt and water thrown into the air by tens of feet. President James Madison and his wife Dolly felt the quake in the White House while church bells rang in Boston due to the shaking there.
But the quakes didn’t end there. From December 16, 1811 through to March of 1812, there were over 2,000 earthquakes reported in the central Midwest with 6,000-10,000 earthquakes located in the “Bootheel” of Missouri where the New Madid Seismic Zone is centered.
The second principal shock, a magnitude 7.8, occurred in Missouri weeks later on January 23, 1812, and the third, a 8.8, struck on February 7, 1812, along the Reelfoot fault in Missouri and Tennessee.
The main earthquakes and the intense aftershocks created significant damage and some loss of life, although lack of scientific tools and news gathering of that era weren’t able to capture the full magnitude of what had actually happened. Beyond shaking, the quakes also were responsible for triggering unusual natural phenomena in the area: earthquake lights, seismically heated water, and earthquake smog.
Residents in the Mississippi Valley reported they saw lights flashing from the ground. Scientists believe this phenomena was “seismoluminescence”; this light is generated when quartz crystals in the ground are squeezed. The “earthquake lights” were triggered during the primary quakes and strong aftershocks.
Water thrown up into the air from the ground, or the nearby Mississippi River, was also unusually warm. Scientists speculate that intense shaking and the resulting friction led to the water to heat, similar to the way a microwave oven stimulates molecules to shake and generate heat. Other scientists believe as the quartz crystals were squeezed, the light they emit also helped warm the water.
During the strong quakes, the skies turned so dark that residents claimed lit lamps didn’t help illuminate the area; they also said the air smelled bad and was hard to breathe. Scientists speculate this “earthquake smog” was caused by dust particles rising up from the surface, combining with the eruption of warm water molecules into the cold winter air. The result was a steamy, dusty cloud that cloaked the areas dealing with the quake.
The February earthquake was so intense that boaters on the Mississippi River reported that the flow of the water there reversed for several hours.
The area remains seismically active and scientists believe another strong quake will impact the region again at some point in the future. Unfortunately, the science isn’t mature enough to tell whether that threat will arrive next week or in 50 years. Either way, with the population of New Madrid Seismic Zone huge compared to the sparsely populated area of the early 1800s, and tens of millions more living in an area that would experience significant ground shaking, there could be a very significant loss of life and property when another major quake strikes here again in the future.